Solar Power and Kilowatt-Hours (kWh) Explained
Understanding Solar Power Use and Kilowatt-Hours (kWh)
Updated: February 16, 2026
What is kWH or Kilowatt-Hours? Electricity usage is an important part of managing your home’s energy use. The term “kilowatt-hours” (kWh) often shows up on utility bills and in talks about solar energy. Understanding the relationship between solar power & kilowatt-hours (kWh) is essential for anyone looking to reduce their energy costs or explore renewable energy options. Remember that Solar Topps provides Residential and Commercial Service for all of Arizona.
We are located in Downtown Phoenix, Arizona. We do specialize in the major cities of Scottsdale, Paradise Valley, Fountain Hills, Peoria, Buckeye, Goodyear, Anthem, Cave Creek, and many others!
If you are interested in Solar, please Contact Us. You can also fill out a Residential and Commercial Quote.
What is kWh a measure of?
Kilowatt-hours are a standard unit of measurement for electric power, widely used to quantify home electricity consumption, solar energy production, and electric vehicle (EV) battery capacity. Breaking down the term: a kilowatt is 1,000 watts, and an hour is 60 minutes. Therefore, a kilowatt-hour represents 1,000 watts used over one hour. Make sure to contact Solar Topps in Phoenix, AZ to learn more about how to measure your kWh usage.
How to Measure kWh Usage for Household Appliances
To measure kWh usage for household appliances, you can use a plug-in electricity usage monitor. These devices are easy to use and provide real-time data on an appliance’s energy consumption. Simply plug the monitor into an outlet, then connect your appliance to the monitor. Over a set period, it will calculate how many kilowatt-hours the appliance has consumed. This allows you to identify which devices use the most energy and adjust your usage accordingly.
Estimating kWh Manually
You can also calculate kWh manually if you know the wattage of your appliance and the number of hours it is used per day. Multiply the wattage by the hours of use, then divide the result by 1,000 to convert the value into kilowatt-hours. For instance, a 100-watt light bulb running for 10 hours would consume 1 kWh (100 watts × 10 hours ÷ 1,000 = 1 kWh). This method can help you estimate energy usage without the need for specialized equipment.
What is 1 kWh of electricity equal to?
To grasp what 1 kWh of electricity entails, consider the device’s wattage and its runtime. For instance, a 500-watt device running for one hour consumes 500 watt-hours or 0.5 kWh. After two hours, it uses 1 kWh. Similarly, a 2,000-watt (2 kW) device would consume 1 kWh in just 30 minutes.
Here’s a table illustrating typical home devices’ wattages and their approximate run times to consume 1 kWh:
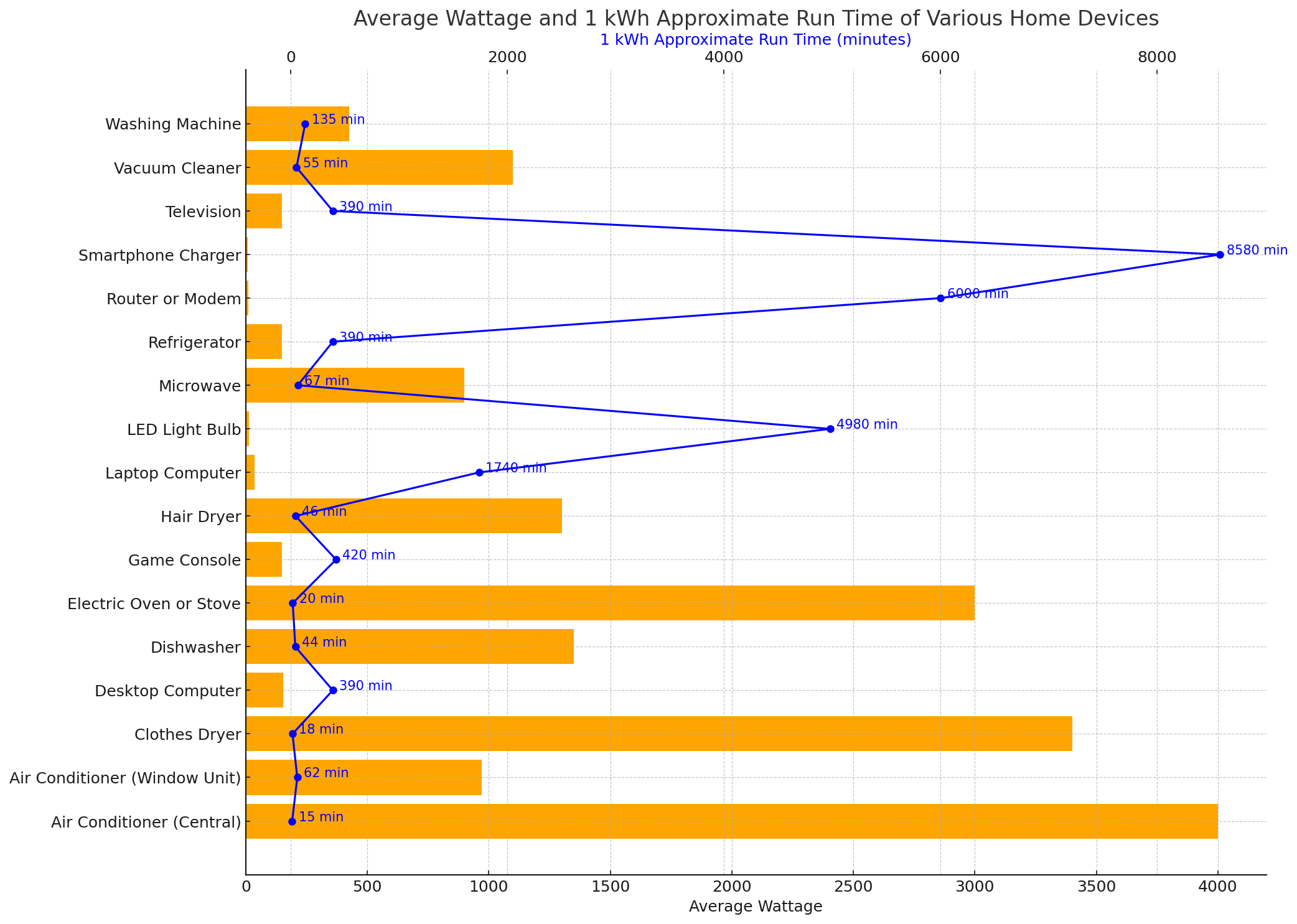
Monthly Electric Bills and kWhs: Solar Power Kilowatt Hours
In the United States, the average household uses about 900 kWh per month to power various appliances, lights, and electronics. This consumption can vary widely based on home size, appliance efficiency, seasonal changes, and energy habits.
How many kWh per day is normal?
On average, an Arizona household consumes around 10,800 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity each year, which translates to an approximate daily usage of 29.5 kWh. This energy usage is not evenly distributed throughout the year, as it typically peaks during the summer and winter months. These seasonal increases are primarily driven by the widespread use of air conditioning systems in the hotter months and the heavy reliance on heating systems during colder periods.
The Geolocation of a Home Matters in Daily Energy Usage
The geographic location of a home plays a crucial role in determining the overall energy consumption. For instance, households located in the hot and humid Southern states of the U.S. tend to experience the highest daily kWh usage due to the constant demand for cooling systems to combat the intense heat and humidity commonly found in this region.
The Average Cost per kWh in Phoenix, Arizona
In Phoenix, Arizona, the average cost of electricity per kilowatt-hour (kWh) typically ranges between $0.12 and $0.15, depending on the time of year and the energy provider. This pricing is influenced by factors such as demand, seasonal fluctuations, and the use of renewable energy sources. These rates place Phoenix within the national average but can lead to higher overall utility bills during summer due to the extensive use of cooling systems to combat the extreme desert heat.
How do you calculate the cost per kWh?
To determine your electricity cost per kWh, divide your total utility bill (excluding fixed fees and taxes) by your total kWh consumption. The kWh rate is usually listed on your bill. Some regions have variable rates based on time of use (TOU) or demand-based pricing, where rates are higher during peak hours. Shifting high-wattage appliance use to non-peak times can help reduce costs.
Average Cost Per kWh in the US
As per the US Energy Information Administration (EIA), the average residential electricity cost in the US was about 12.36 cents per kWh in 2022. Rates vary significantly by state, with Hawaii having the highest at 39.72 cents and Wyoming the lowest at 8.24 cents per kWh. By February 2024, the US Bureau of Labor Statistics reported an average residential electricity price of 17.3 cents per kWh.
Solar Panel kWh Explained
The kWh produced by your solar panels can offset the kWh you purchase from the utility, lowering your energy bills. The value of these solar kWh credits depends on your utility’s net metering or net billing policies. To estimate solar kWh production, use the formula: Total System Wattage x Number of Peak Sun Hours. For example, a 6.8 kW system in an area with 5 peak sun hours per day would generate about 34 kWh daily.
Learn More About How Solar Can Transform Your Electric Bill
If you’re interested in reducing your monthly kWh usage through solar energy, reach out to a home energy expert at Solar Topps.




 Published: Jun 10, 2024
Published: Jun 10, 2024





